A sitemap is an XML file that informs search engines such as Google, about the pages of your website, their relevance, and how frequently they are updated. Using sitemaps facilitates crawlers indexing the site, therefore sitemap plays a crucial role in modern SEO (Search Engine Optimization).
Creating Sitemaps in Django
Considering the scope of the article I am assuming you have basic knowledge of Django and have a project up and running if not read the following article first.
Installation
Add 'django.contrib.sitemaps' in INSTALLED_APPS settings.py.
# config/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'django.contrib.sites', # new
'django.contrib.sitemaps', # new
'blog',
]
SITE_ID = 1 # new
Make sure your TEMPLATES setting contains a DjangoTemplates backend whose APP_DIRS options are set to True. It's in there by default, revert it in case you have changed it.
Creating Sitemap
I am generating a sitemap for a blog application following is the models.py file for reference.
class Post(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=200, unique=True)
slug = models.SlugField(max_length=200, unique=True)
author = models.ForeignKey(
User, on_delete=models.CASCADE, related_name="blog_posts"
)
updated_on = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
content = models.TextField()
created_on = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
class Meta:
ordering = ["-created_on"]
def __str__(self):
return self.title
def get_absolute_url(self):
return reverse('read-more', kwargs={'slug': self.slug})
URLs
There are two URL files to update: our top-level one at projects/urls.py and then one within the recipes app that must be created. Let's create that new one now.
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
from django.contrib.sitemaps import GenericSitemap # for site map
from django.contrib.sitemaps.views import sitemap # for site map
info_dict = {
'queryset': Blog.objects.all(),
}
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', include('blog.urls')),
path('sitemap.xml', sitemap, # for site map
{'sitemaps': {'blog': GenericSitemap(info_dict, priority=1)}},
name='django.contrib.sitemaps.views.sitemap'),
]
Make sure the server is running and visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/sitemap.xml.
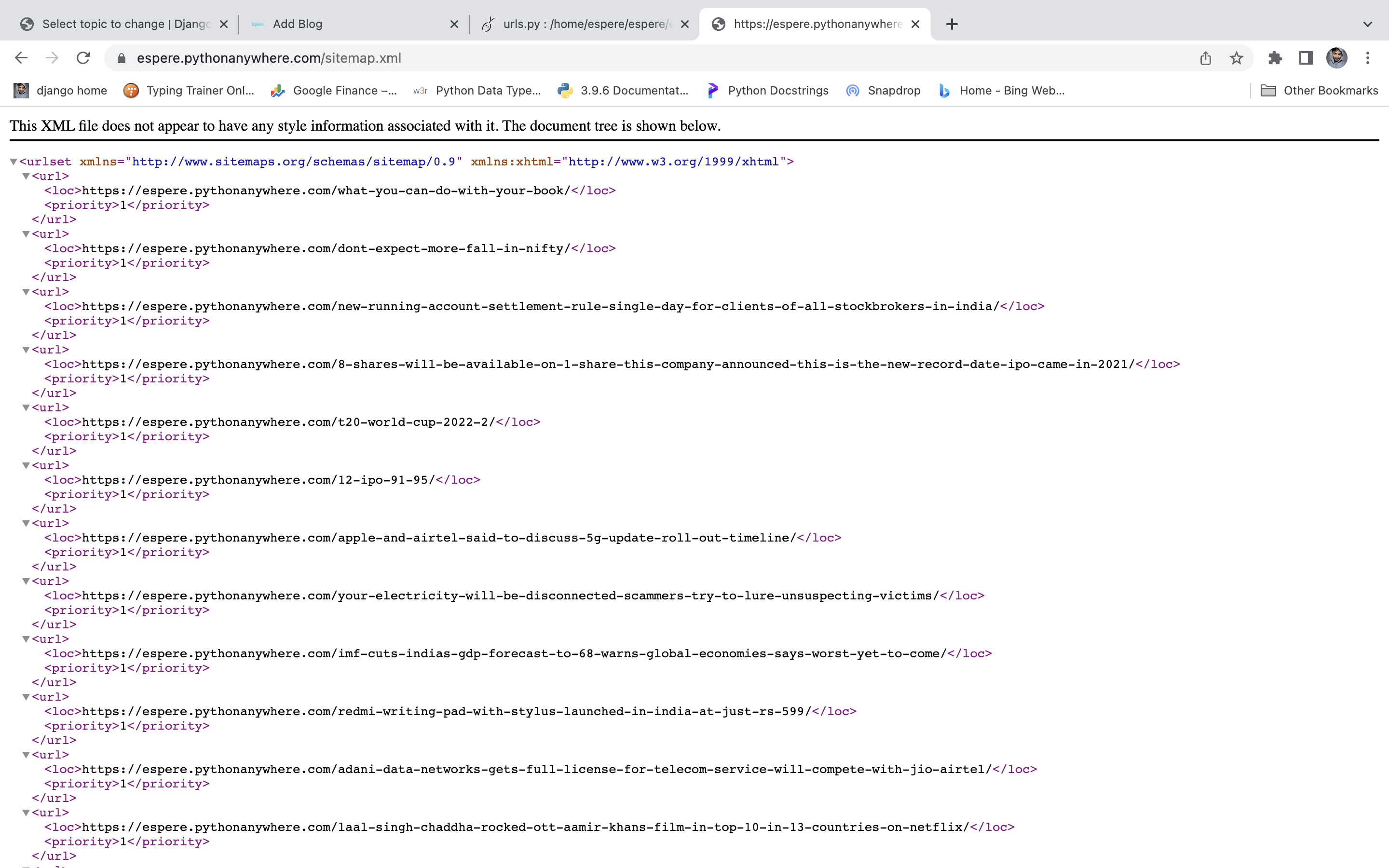
There's our sitemap! But notice that it's used https://espere.pythonanywhere.com/ as the name of our site. This comes from the sites framework. If you go into the Django admin, there's a new section called Sites where you can change the name.
It's also possible to change the priority and changefreq. And while you might notice that the current version uses http rather than https, if your production site uses https then that will be reflected in the sitemap. Or you can change the protocol entirely, if so desired.